2023年3月,印度德里印度理工学院化学系酶和微生物生物化学实验室Huma Fatima等人在Journal of Environmental Management(IF=8.91)发表题为 “Efficient remediation of meropenem using Bacillus tropicus EMB20 β-lactamase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles”的文章。该文章报道了一种采用共价偶联法将来自Bacillus tropicus EMB20的β-内酰胺酶固定在磁性纳米颗粒(Fe3O4)上,来降解污染系统中β-内酰胺类抗生素的方法。通过SEM、FTIR、UV-Vis、XRD对纳米共价偶联物进行了结构表征。制备的酶纳米共价偶联物可在 3小时内完全去除10 mg/L的美罗培南。此外,固定化酶成功地被回收并重复使用了5个循环,去除效率为57%。通过微生物MTT法、共聚焦显微镜和生长研究,发现其水解产物对细菌无毒。纳米共价偶联物还在2小时内对模拟水产养殖废水中的混合抗生素完全去除。总的来说,该研究所制备的纳米共价偶联物可用于环境样品中β-内酰胺类抗生素的高效降解。
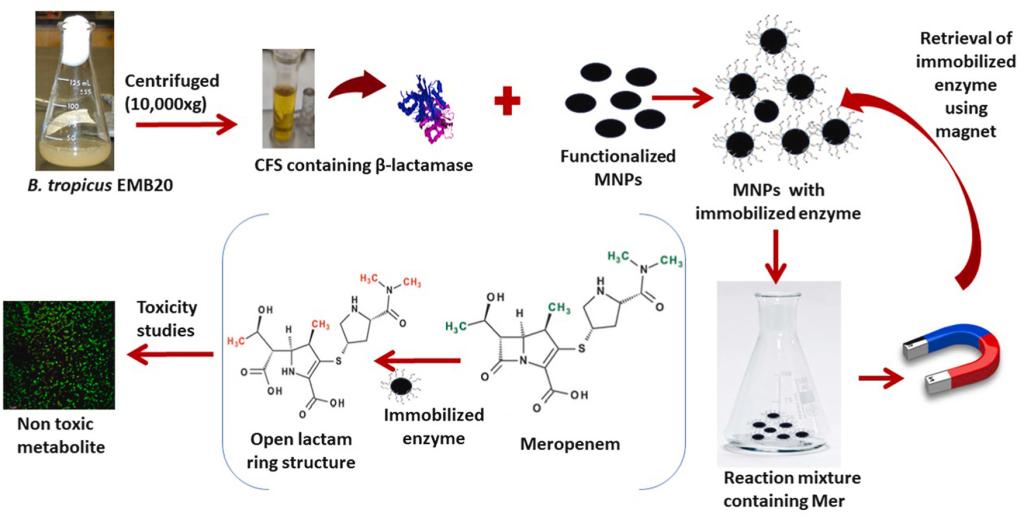
Graphical abstract
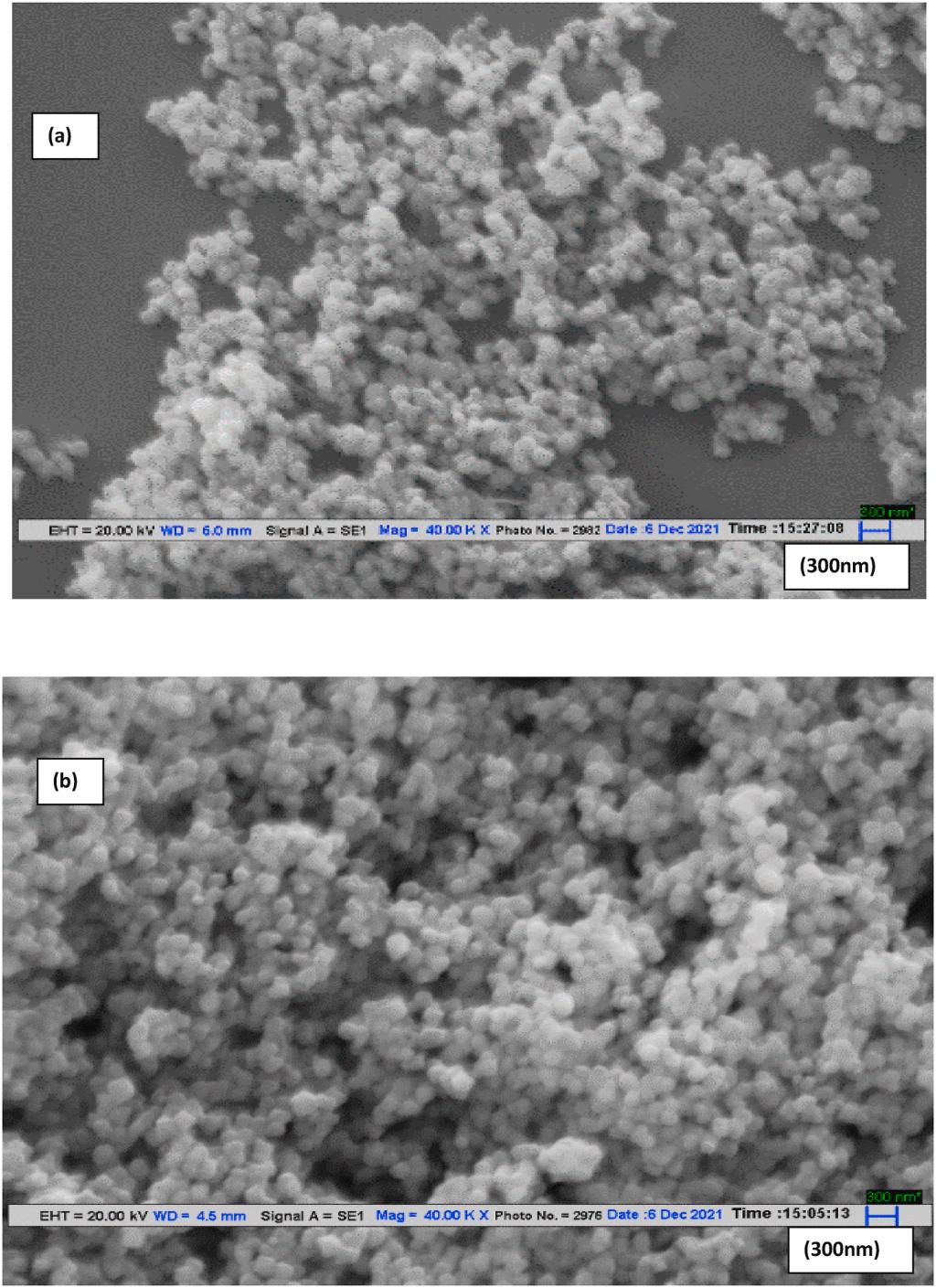
Fig. 1. Scanning electron micrographs of magnetic nanoparticles (a) and, β-lactamase immobilized magnetic nanoparticles (b).
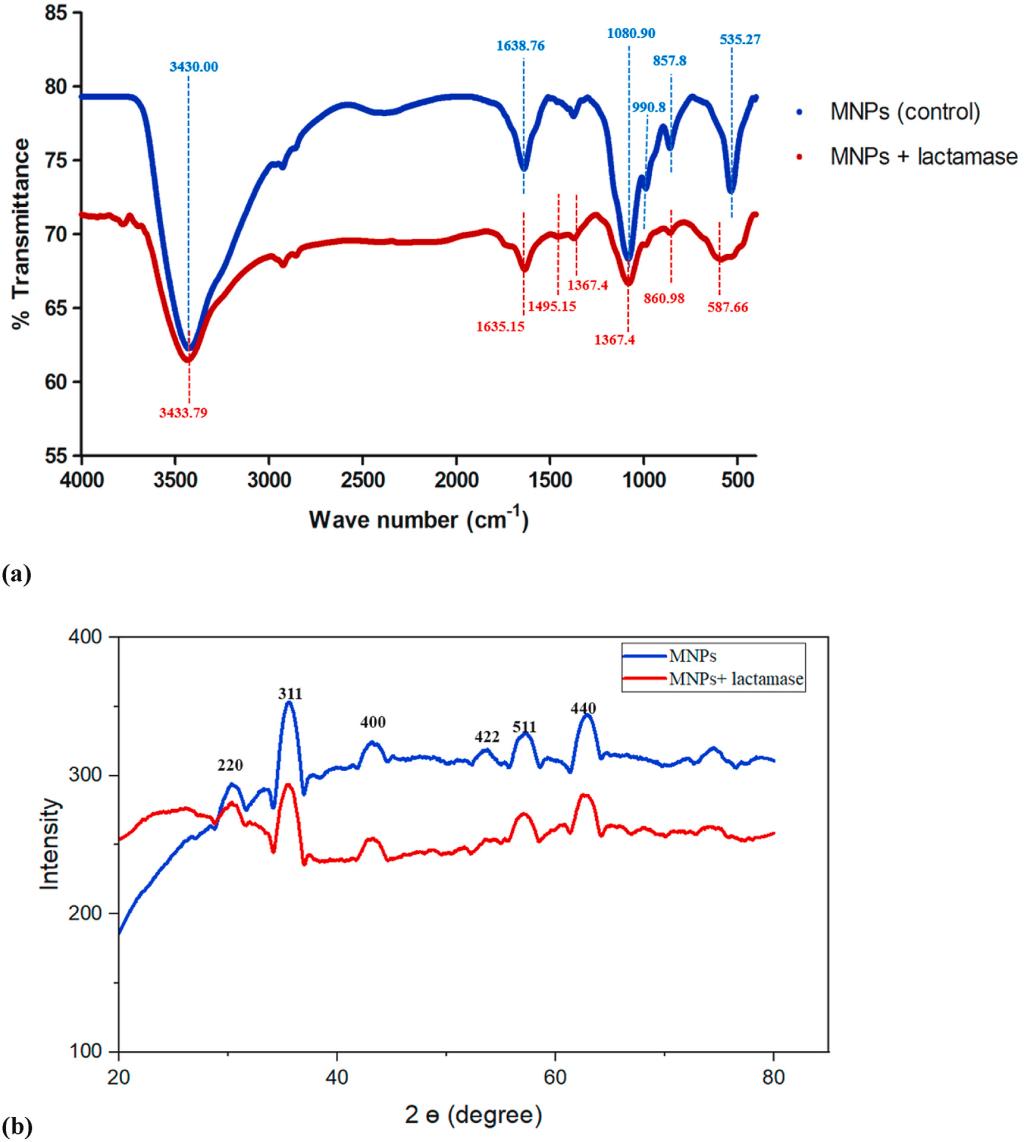
Fig. 2. FT-IR spectra (a) and X-ray diffractogram (b) of unbound magnetic nanoparticles (blue) and β-lactamase immobilized magnetic nanoparticles (red). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
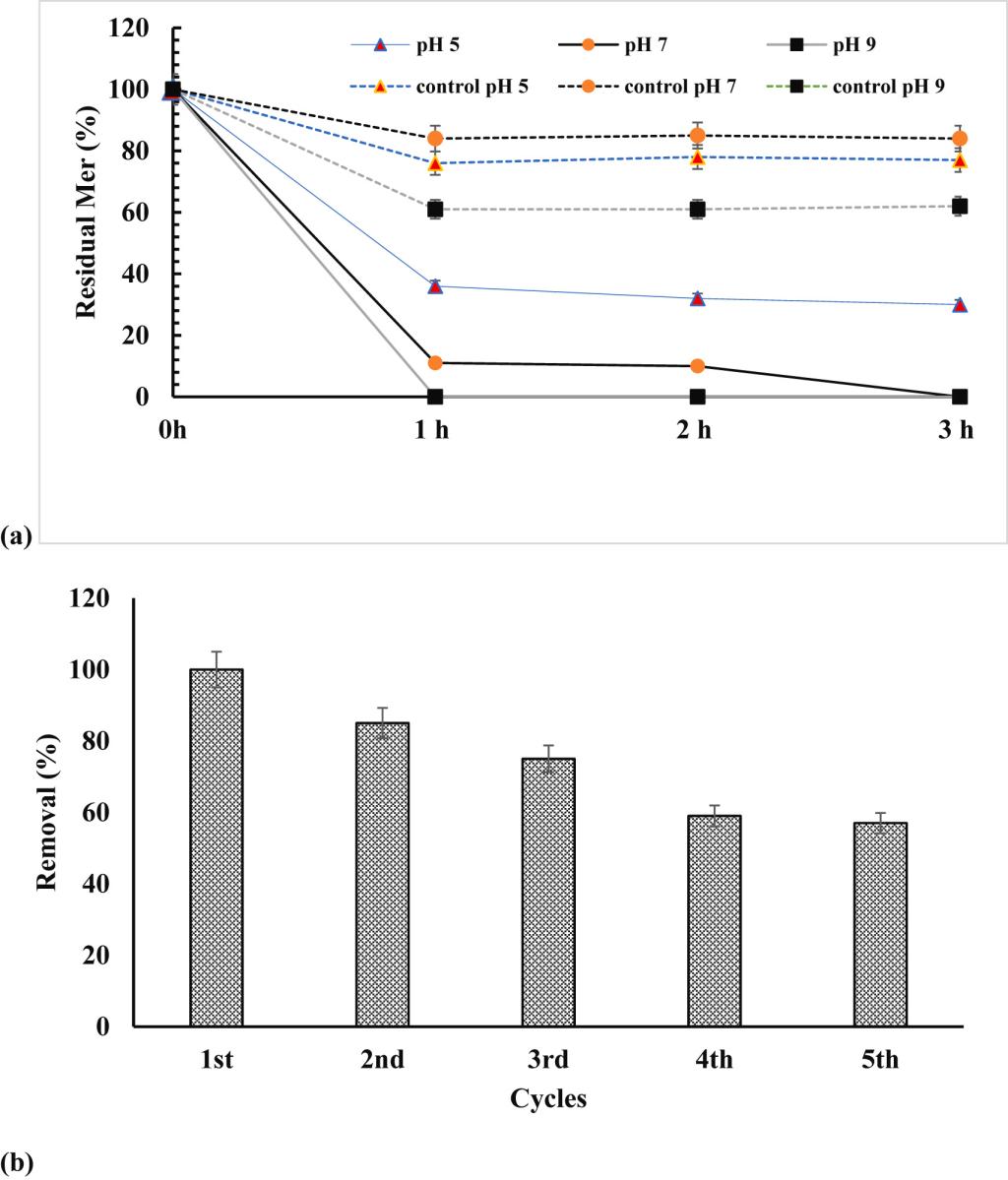
Fig. 4. Use of enzyme immobilized MNPs in removal of Mer under varying pH (a) and repeated cycles (b).
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117054
原文链接:Efficient remediation of meropenem using Bacillus tropicus EMB20 β-lactamase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles - ScienceDirect